Cars are one of the most common and convenient modes of transportation in the world. They are also complex machines that involve various components and systems working together to provide power, speed, and safety. In this article, we will explore how cars run, from the engine to the wheels, and how different types of vehicles have different applications and advantages.
The engine is the main source of power for the car. It converts the chemical energy of the fuel into mechanical energy that moves the pistons and crankshaft. The engine can be classified into two main types: internal combustion engine and electric motor.
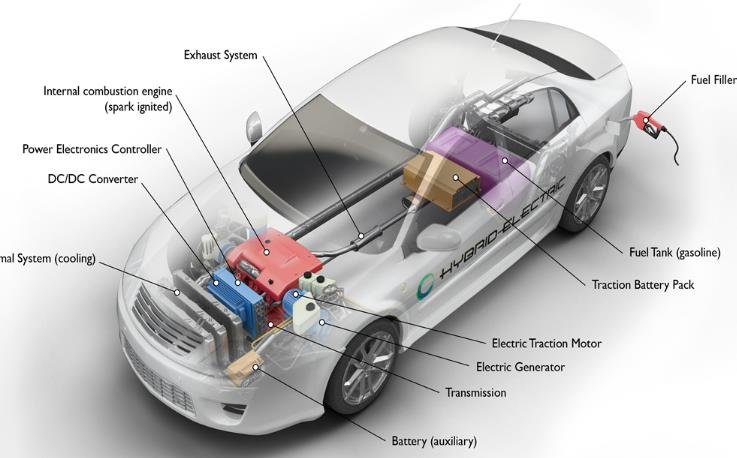
Internal Combustion Engine
An internal combustion engine (ICE) burns fuel inside the cylinders, creating hot gases that expand and push the pistons. The pistons are connected to the crankshaft, which rotates and transfers the power to the transmission. The most common fuels for ICE are gasoline and diesel, which have high energy density and can provide long range and high performance. However, ICE also produce harmful emissions and noise, and require regular maintenance and oil changes.
Electric Motor
An electric motor uses electricity to create a magnetic field that rotates the rotor. The rotor is connected to the shaft, which transfers the power to the transmission. The electricity for the electric motor can come from a battery, a fuel cell, or an external source. Electric motors are more efficient, quieter, and cleaner than ICE, but they have lower energy density and require frequent charging or refueling.
The Transmission: The Brain of the Car
The transmission is the system that controls the speed and torque of the car. It connects the engine to the drive shaft, which delivers the power to the wheels. The transmission can be manual or automatic, and can have different numbers of gears or speeds.
Manual Transmission
A manual transmission requires the driver to shift gears manually using a clutch and a gear lever. The clutch disengages the engine from the transmission, allowing the driver to select the appropriate gear for the speed and terrain. The manual transmission gives the driver more control and feedback, and can be more fuel-efficient and fun to drive. However, it also requires more skill and attention, and can be tiring and stressful in heavy traffic.
Automatic Transmission
An automatic transmission shifts gears automatically using a torque converter and a computer. The torque converter is a fluid coupling that transfers the power from the engine to the transmission without a clutch. The computer monitors the speed, load, and throttle position, and selects the optimal gear for the driving conditions. The automatic transmission is easier and more comfortable to drive, and can be smoother and faster than manual transmission. However, it can also be less responsive and less fuel-efficient, and can cost more to repair and maintain.
The Drive Train: The Muscles of the Car
The drive train is the system that transfers the power from the transmission to the wheels. It consists of the drive shaft, the differential, and the axles. The drive train can be front-wheel drive, rear-wheel drive, or all-wheel drive, depending on which wheels receive the power.
Front-Wheel Drive
A front-wheel drive (FWD) car has the engine, transmission, and drive train all located in the front of the car. The drive shaft connects the transmission to the differential, which splits the power to the front wheels. The front wheels provide both propulsion and steering, making the car more compact and lighter. FWD cars are more fuel-efficient, cheaper, and easier to handle in slippery conditions. However, they can also suffer from understeer, torque steer, and reduced traction and stability at high speeds.
Rear-Wheel Drive
A rear-wheel drive (RWD) car has the engine and transmission in the front of the car, but the drive train in the rear. The drive shaft connects the transmission to the differential, which splits the power to the rear wheels. The rear wheels provide propulsion, while the front wheels provide steering, making the car more balanced and agile. RWD cars are more responsive, faster, and more fun to drive. However, they can also be less fuel-efficient, more expensive, and harder to control in slippery conditions.
All-Wheel Drive
An all-wheel drive (AWD) car has the engine, transmission, and drive train distributed among all four wheels. The drive shaft connects the transmission to a center differential, which splits the power to the front and rear differentials, which further split the power to the individual wheels. The AWD system can vary the power distribution among the wheels, depending on the driving conditions and the driver’s input. AWD cars are more versatile, stable, and capable in various terrains and weather. However, they can also be heavier, more complex, and more costly to buy and maintain.
The Wheels: The Feet of the Car
The wheels are the parts of the car that make contact with the road. They consist of the tires, the rims, and the brakes. The wheels are responsible for providing traction, steering, and braking, as well as absorbing shocks and vibrations.
Tires
The tires are the rubber casings that cover the rims and contain pressurized air. The tires have tread patterns that create friction with the road surface, allowing the car to accelerate, turn, and stop. The tires also have grooves that channel water and debris away from the contact patch, improving the grip and preventing hydroplaning. The tires can have different sizes, shapes, and compounds, depending on the type and purpose of the car. The tires need to be properly inflated, aligned, and rotated, to ensure optimal performance and safety.
Rims
The rims are the metal or alloy structures that support the tires and attach them to the axles. The rims have spokes that allow air to flow through and cool the brakes. The rims also have valves that allow air to enter and exit the tires. The rims can have different designs, colors, and finishes, depending on the style and preference of the car owner. The rims need to be clean, balanced, and free of cracks and dents, to ensure smooth and stable driving.
Brakes
The brakes are the devices that slow down or stop the car by applying friction to the wheels. The brakes can be disc or drum, and can have different components and systems, depending on the type and performance of the car.
Disc Brakes
Disc brakes have a metal disc called a rotor that rotates with the wheel, and a metal caliper that holds a pair of brake pads that squeeze the rotor when the brake pedal is pressed. The friction between the pads and the rotor creates heat and reduces the speed of the wheel. Disc brakes are more effective, responsive, and durable than drum brakes, but they can also be more expensive and prone to fading and warping.
Drum Brakes
Drum brakes have a metal drum that rotates with the wheel, and a metal cylinder that holds a pair of brake shoes that press against the inner surface of the drum when the brake pedal is pressed. The friction between the shoes and the drum creates heat and reduces the speed of the wheel. Drum brakes are cheaper, simpler, and more self-adjusting than disc brakes, but they can also be less efficient, less reliable, and more susceptible to overheating and locking.
The Applications: The Uses of the Car
Cars have different applications and advantages, depending on their type, design, and features. Some of the common types of cars are:
Sedan
A sedan is a car that has four doors and a separate trunk. It can seat four to five passengers, and has a comfortable and spacious interior. Sedans are ideal for family, business, and personal use, as they offer a smooth and quiet ride, good fuel economy, and ample cargo space. However, sedans can also be less exciting, less versatile, and less maneuverable than other types of cars.
Hatchback
A hatchback is a car that has two or four doors and a rear door that opens upward. It can seat four to five passengers, and has a flexible and roomy interior. Hatchbacks are ideal for urban, sporty, and practical use, as they offer a fun and agile drive, good visibility, and easy access to the cargo area. However, hatchbacks can also be less refined, less secure, and less spacious than other types of cars.
SUV
An SUV is a car that has a high ground clearance, a large body, and a powerful engine. It can seat five to seven passengers, and has a rugged and luxurious interior. SUVs are ideal for off-road, adventure, and family use, as they offer a strong and stable drive, good safety, and generous cargo and passenger space. However, SUVs can also be less efficient, less eco-friendly, and less agile than other types of cars.
Coupe
A coupe is a car that has two doors and a sloping roofline. It can seat two to four passengers, and has a sporty and stylish interior. Coupes are ideal for performance, luxury, and personal use, as they offer a fast and thrilling drive, good aerodynamics, and attractive looks. However, coupes can also be less practical, less comfortable, and less accessible than other types of cars.
Convertible
A convertible is a car that has a retractable roof that can be opened or closed. It can seat two to four passengers, and has a breezy and elegant interior. Convertibles are ideal for leisure, entertainment, and enjoyment use, as they offer a fun and exhilarating drive, good visibility, and a sense of freedom. However, convertibles can also be less safe, less quiet, and less spacious than other types of cars.
